Summary
| Title | ADF/cofilin influences actin filament turnover |
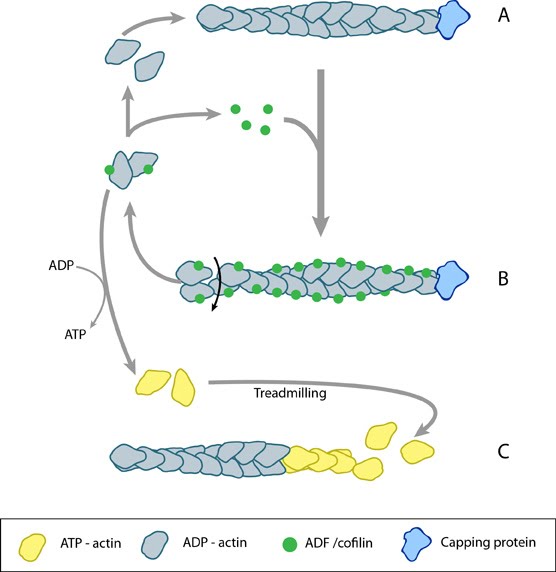
| Description | ADF/cofilin influences actin filament turnover. ADF cooperatively binds to F-actin to increase the steady state turn-over (e.g. treadmilling rate) of actin filaments and accumulation of ADF-ADP-G-actin, ADP-G-actin, and ATP-G-actin (via nucleotide exchange). ADF binds faster to actin filaments that have barbed end capping proteins (e.g. gelsolin) (B). The actin subunits depolymerizing from ADF-bound filaments are recycled to filaments lacking ADF, thus maintaining the pool of actin-filaments. At high ADF concentration, polymerization of ADP-actin at the pointed end is favored on capped-filaments (A); alternatively, nucleotide exchange increases the pool of ATP-actin for barbed end assembly of new or existing filaments (C). |
| Date | 2011 |
| Referred pages | Actin Filament Depolymerization |
| License | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License |
| Permission | Modification, copying and distribution (commercial) of this image is strictly prohibited without written consent. Please contact MBInfo at [email protected] to request permission to use this image. |
How to cite this page?
ADF/cofilin influences actin filament turnover. In MBInfo Wiki, Retrieved 10/21/2014 from http://mbinfo.mbi.nus.edu.sg/figure/1384241425959/