Summary
| Title | Actin binding proteins influence actin dynamics |
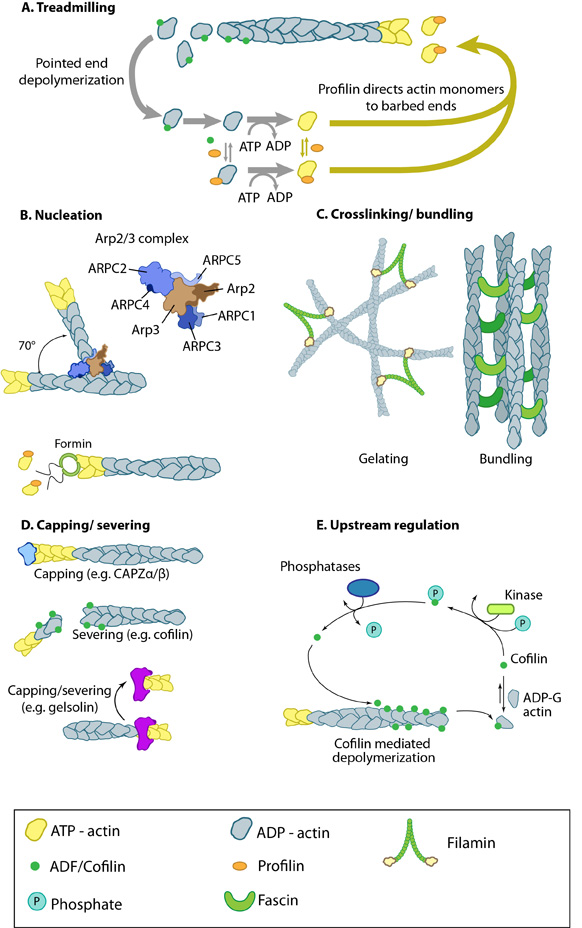
| Description | A. Treadmilling of actin filaments can be altered by profilin and ADF which generally increase and decrease the size of actin filaments, respectively. B. New filaments are nucleated by the ARP2/3 complex, which binds both G-actin monomers and the side of actin filaments to nucleate new filaments or branches. Formins nucleate new filaments by binding G-actin and through cooperation with profilin. C. Actin cross-linking proteins influence the packing and organization of actin filaments into secondary structures. D. Capping and severing proteins promote disassembly of actin filaments. E. Actin filament assembly can be modulated by events such as controlled nucleotide hydrolysis (e.g. ATP on actin) and reversible modifications (e.g. phosphorylation) on components that control actin assembly. |
| Date | 2011 |
| Referred pages | Actin Filament Elongators |
| License | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License |
| Permission | Modification, copying and distribution (commercial) of this image is strictly prohibited without written consent. Please contact MBInfo at [email protected] to request permission to use this image. |
How to cite this page?
Actin binding proteins influence actin dynamics. In MBInfo Wiki, Retrieved 10/21/2014 from http://mbinfo.mbi.nus.edu.sg/figure/1384242015241/