Summary
| Title | Filopodia can pull objects |
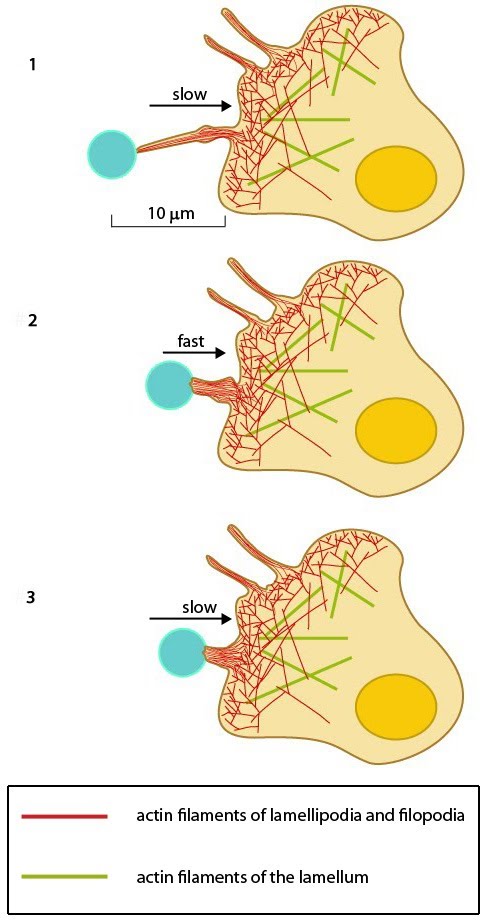
| Description | After a filopodium binds to an object, retrograde actin movement and myosin motor activity provide the force(s) needed for pulling the object towards the cell body. Once pulling starts, the initial slow movement (#1) is followed by a burst of rapid movement (#2) that diminishes as the object reaches the cell body (#3) [2]. |
| Date | 2011 |
| Referred pages | Filopodium Assembly |
| License | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License |
| Permission | Modification, copying and distribution (commercial) of this image is strictly prohibited without written consent. Please contact MBInfo at feedback@mechanobio.info to request permission to use this image. |
How to cite this page?
Filopodia can pull objects. In MBInfo Wiki, Retrieved 10/21/2014 from http://mbinfo.mbi.nus.edu.sg/figure/1384242261468/