Summary
| Title | Structure of G-actin and its assembly into filaments |
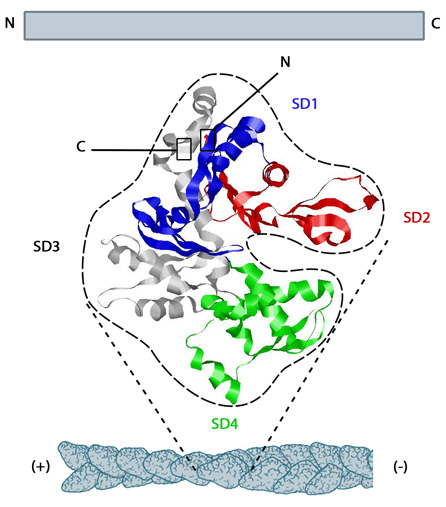
| Description | The structure shown here [3] was downloaded from the RSCB Protein Data Bank (PDB file: 1atn). The ATP binding cleft is starred (*) on the right. Actin comprises four subdomains, termed SD1 (blue), SD2 (red), SD3 (grey) and SD4 (green). The barbed end of each monomer (SD1 and SD3) is shown on the left and the pointed end (SD2 and SD4) is shown on the right. Similarly the polarity of the actin filament, which comprises these monomers is shown at the bottom, with the barbed (+) end on the left and the pointed (-) end on the right. |
| Date | 2013 |
| Referred pages | Actin Filament Elongators |
| License | Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License |
| Permission | Modification, copying and distribution (commercial) of this image is strictly prohibited without written consent. Please contact MBInfo at [email protected] to request permission to use this image. |
How to cite this page?
Structure of G-actin and its assembly into filaments. In MBInfo Wiki, Retrieved 10/21/2014 from http://mbinfo.mbi.nus.edu.sg/figure/1385018442649/