Additional Links
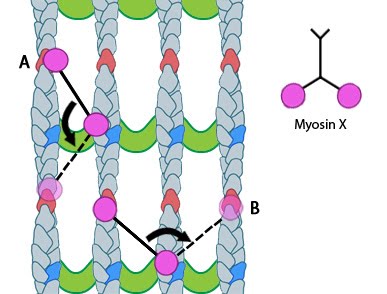
| Functional Module: Myosin-X in the Transport of Cargo and Filopodia Initiation
Filopodia are motile structures that
contribute to the cell’s ability to detect mechanical or chemical
signals and measure and respond to its physical environment. This
mechanosensing is mediated primarily by adhesions and receptor molecules
located at the tips, or along the shafts, of filopodia. |
References
- Berg JS. & Cheney RE. Myosin-X is an unconventional myosin that undergoes intrafilopodial motility. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002; 4(3):246-50. [PMID: 11854753]
- Tokuo H. & Ikebe M. Myosin X transports Mena/VASP to the tip of filopodia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004; 319(1):214-20. [PMID: 15158464]
- Zhang H., Berg JS., Li Z., Wang Y., Lång P., Sousa AD., Bhaskar A., Cheney RE. & Strömblad S. Myosin-X provides a motor-based link between integrins and the cytoskeleton. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004; 6(6):523-31. [PMID: 15156152]
- Zhu XJ., Wang CZ., Dai PG., Xie Y., Song NN., Liu Y., Du QS., Mei L., Ding YQ. & Xiong WC. Myosin X regulates netrin receptors and functions in axonal path-finding. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007; 9(2):184-92. [PMID: 17237772]
- Bohil AB., Robertson BW. & Cheney RE. Myosin-X is a molecular motor that functions in filopodia formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2006; 103(33):12411-6. [PMID: 16894163]
- Nagy S., Ricca BL., Norstrom MF., Courson DS., Brawley CM., Smithback PA. & Rock RS. A myosin motor that selects bundled actin for motility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008; 105(28):9616-20. [PMID: 18599451]
- Ricca BL. & Rock RS. The stepping pattern of myosin X is adapted for processive motility on bundled actin. Biophys. J. 2010; 99(6):1818-26. [PMID: 20858426]
- Hirano Y., Hatano T., Takahashi A., Toriyama M., Inagaki N. & Hakoshima T. Structural basis of cargo recognition by the myosin-X MyTH4-FERM domain. EMBO J. 2011; 30(13):2734-47. [PMID: 21642953]
- Watanabe TM., Tokuo H., Gonda K., Higuchi H. & Ikebe M. Myosin-X induces filopodia by multiple elongation mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2010; 285(25):19605-14. [PMID: 20392702]