| 1 | β-catenin | | |
| 2 | β-catenin at the cell membrane | |  |
| 3 | Alpha (α)-catenin | | 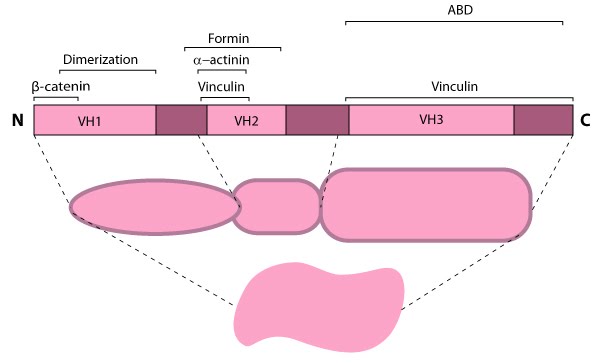 |
| 4 | Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) | | 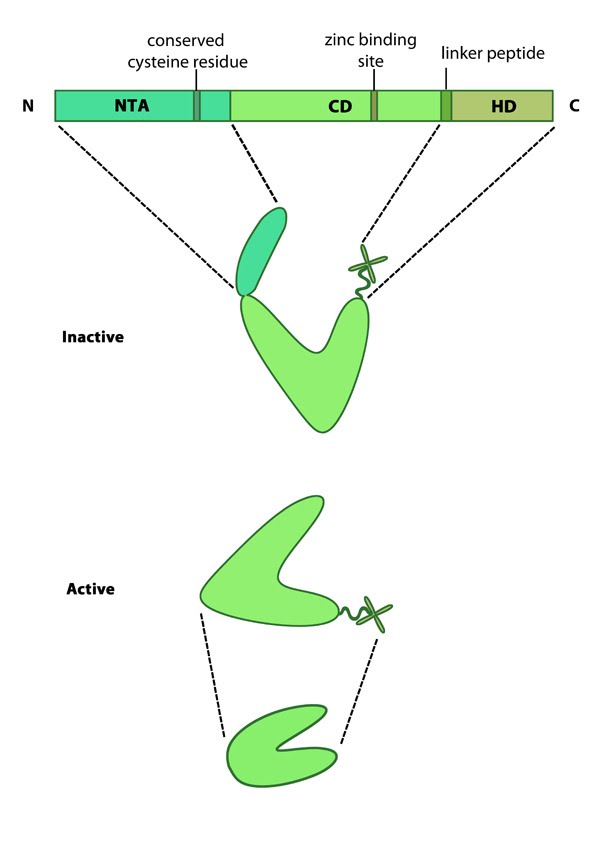 |
| 5 | Variations in MMP structure | | 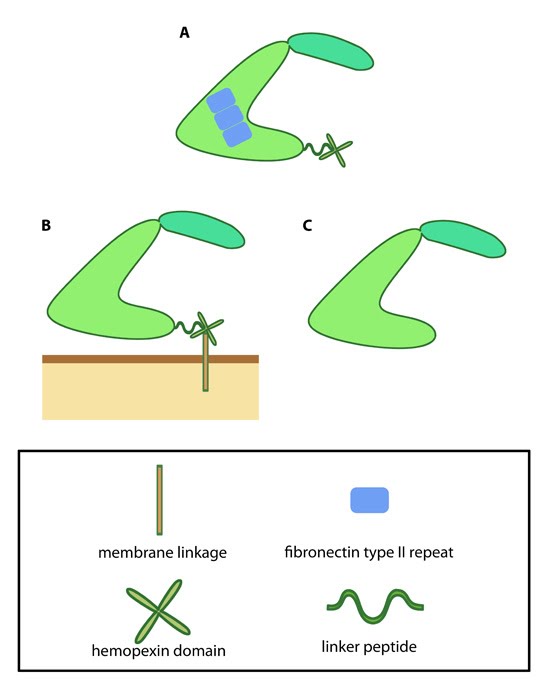 |
| 6 | Zyxin | | 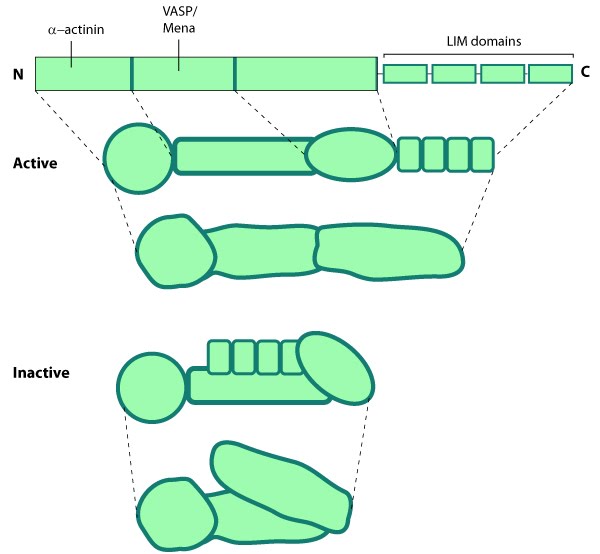 |
| 7 | Zyxin cellular localization | |  |
| 8 | Tensin | |  |
| 9 | Talin | |  |
| 10 | Talin recruitment to membrane | |  |
| 11 | Domain structure of syndecans | |  |
| 12 | Kinesin schematic | |  |
| 13 | Kinesin stepping schematic. | |  |
| 14 | The kinesin powerstroke | |  |
| 15 | IRSp53 | |  |
| 16 | Regulation of Rho GTPase activity | |  |
| 17 | Formin | |  |
| 18 | Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) | |  |
| 19 | Fimbrin | |  |
| 20 | Filamin | |  |
| 21 | Fascin | |  |
| 22 | Ena/VASP family | |  |
| 23 | Cortactin | |  |
| 24 | Multiple roles of cortactin | |  |
| 25 | Capping proteins promote actin filament disassembly | |  |
| 26 | Classical cadherin structure | |  |
| 27 | Types of cadherin interactions | |  |
| 28 | Alpha (α)-actinin | |  |
| 29 | ADF/cofilin influences actin filament turnover | |  |
| 30 | Structure of G-actin and its assembly into filaments | |  |
| 31 | Adherens junctions link actin filaments between cells | |  |
| 32 | Schematic of Amphyphysin structure | |  |
| 33 | IFs are flexible and resistant to force | |  |
| 34 | Intermediate Filament Assembly | |  |
| 35 | Schematic diagram of immunoglobulin superfamily members that are found in neurons. | |  |
| 36 | Growth cone structure | |  |
| 37 | CD1 mouse spinal commissural neuron with growth cone | |  |
| 38 | Cc and actin filament assembly | |  |
| 39 | Cc and assembly of microtubules | |  |
| 40 | Anchoring junctions | |  |
| 41 | Integrins as adhesion receptor in focal adhesion (FA) | |  |
| 42 | Structure of an actin filament showing the barbed (or plus) and pointed (or minus) ends | |  |
| 43 | Actin filament distribution in cells and tissues | |  |
| 44 | Tropomyosin stabilizes thin filaments | |  |
| 45 | Cell cortex (aka cortical actin, actin cortex) | |  |
| 46 | Actin binding proteins influence actin dynamics | |  |
| 47 | Model of filopodia collapse | |  |
| 48 | General structure of phosphoinositides | |  |
| 49 | Phosphoinositides involved in cell signaling | |  |
| 50 | Different types of filopodia | |  |
| 51 | Dynamic behaviors of filopodia | |  |
| 52 | Steps in filopodium formation | |  |
| 53 | Filopodia can pull objects | |  |
| 54 | No adhesion to the substrate limits filopodial protrusion | |  |
| 55 | Adhesion influences filopodia protrusion | |  |
| 56 | Types of adhesions found in filopodia | |  |
| 57 | Lateral movement of filopodia | |  |
| 58 | Adherens junctions of hepatocytes | |  |
| 59 | Electron microscopy image of rat intestinal mucosa epithelial cell-cell junctions | |  |
| 60 | Different Structures of Adherens Junctions | |  |
| 61 | Nectin and nectin-like (Necl) structure | |  |
| 62 | Nectin-nectin and cadherin-cadherin binding properties | |  |
| 63 | ‘Fork initiation and zipper’ model for adherens junction formation | |  |
| 64 | Basic components of the adherens junction. | |  |
| 65 | Cadherin extracellular domain structure. | |  |
| 66 | EC1-EC1 strand swapping. | |  |
| 67 | Cadherin endocytosis upon release of cell-cell contact. | |  |
| 68 | Structure of an invadopodium | |  |
| 69 | Podosomes | |  |
| 70 | Podosome structure | |  |
| 71 | Lamellipodia in a cell stained for F-actin | |  |
| 72 | Structure of the lamellipodium and the lamellum | |  |
| 73 | Conserved steps in cell spreading and movement | |  |
| 74 | Focal Adhesions act as Molecular Clutch during Forward movement | |  |
| 75 | Mediators of mechanosensing | |  |
| 76 | Three phases of filament assembly | |  |
| 77 | Components of the cytoskeleton | |  |
| 78 | Types of cell-matrix adhesion complexes (CMACs) | |  |
| 79 | Stages in focal adhesion formation | |  |
| 80 | Focal adhesion organization | |  |
| 81 | untitled | |  |
| 82 | Adhesion growth under force | |  |
| 83 | Three-dimensional architecture of focal adhesions | |  |
| 84 | Matrix property affects FA dynamics and mechanotransduction | |  |
| 85 | Dynamic instability of microtubules | |  |
| 86 | Microtubules are nucleated by the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) | |  |
| 87 | Structure of the centrosome | |  |
| 88 | Actin-myosin contraction in muscle cells | |  |
| 89 | Stress fiber structure | |  |
| 90 | Myosins have diverse motor protein activity | |  |
| 91 | Accessory proteins control actin filament length | |  |
| 92 | Actin polymerization produces force for movement | |  |
| 93 | Potential mechanosensors in the detection of shear stress by endothelial cells | |  |
| 94 | Overview of mechanotransduction in a cell | |  |
| 95 | Models for force-induced modulation of cytoskeletal stiffness | |  |
| 96 | Mechanical versus chemical signal propagation | |  |
| 97 | Energy state graphs | |  |
| 98 | Thermodynamic model for mechanosensing and self-assembly of focal adhesions | |  |
| 99 | Forces can bring molecules together | |  |
| 100 | Deforming forces initiate mechanotransduction events | |  |
| 101 | Nuclear connectivity and mechanotransduction | |  |
| 102 | Nucleoskeleton stabilizes the nuclear structure. | |  |
| 103 | GTPase signaling at the leading edge mediated by integrin β1 and syndecan-4. | |  |
| 104 | Types of actin filament crosslinking proteins | |  |
| 105 | Myosin-X step size | |  |
| 106 | Formin-mediated nucleation of actin filaments | |  |
| 107 | ADF/cofilin severs actin filaments | |  |
| 108 | Reconstruction of Arp2/3 complex-mediated nucleation | |  |
| 109 | Arp2/3-mediated actin polymerization | |  |
| 110 | Integrin activation | |  |
| 111 | The “power stroke” mechanism for myosin movement along actin filaments | |  |