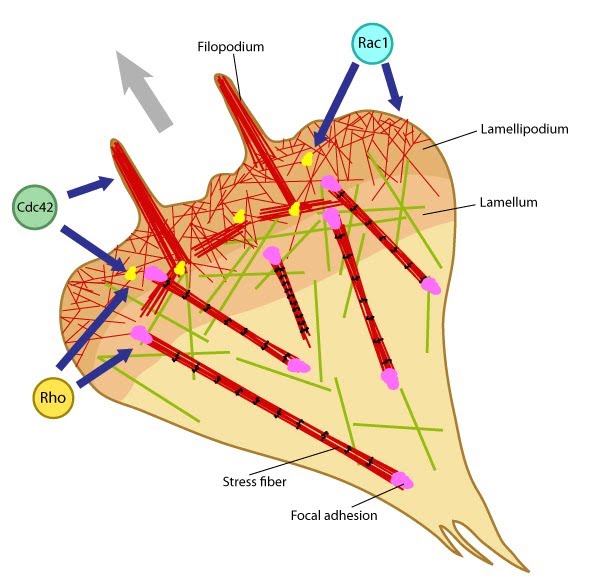
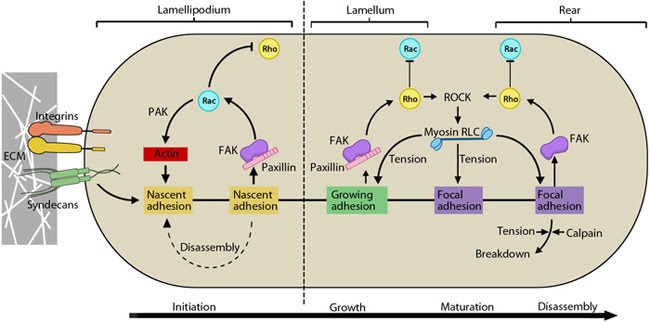
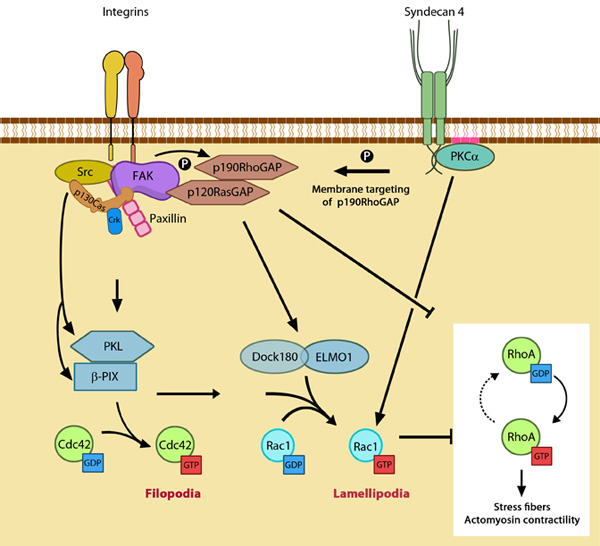
Additional Links Rac activation and Rho suppression are essential for: Focal adhesion initiation Focal adhesions growth Lamellipodial translocation Cdc42 activation and Rho suppression are essential for: Filopodia adherence Rho activation is essential for: Focal adhesion maturation Retraction of the trailing edge and Focal adhesion disassembly Podosome disassembly Cell polarity Influenced by: Guidance signals | Functional module: Integrin β1-syndecan-4 synergy in signaling protrusion and adhesion dynamics
Neither syndecan nor integrin is capable of independently supporting cell adhesion or spreading. Despite the cooperativity of integrin-syndecan pairs in various contexts (reviewed in [1]), recent studies have established synergistic signaling by integrin β1 and syndecan-4; they play cooperative yet distinct roles in cell spreading and maturation of adhesions as well as directional migration respectively [2, 3]. The receptors co-localize in early adhesion sites at the leading edge with ligand binding by both receptors (e.g fibronectin binds via cell binding domain [RGD] to integrin and via HepII domain to syndecan) being necessary for downstream signaling [4, 5]. This is crucial as the cell polarity and migration is determined by differentially regulating signals at the leading and trailing edges. |
References
- Morgan MR., Humphries MJ. & Bass MD. Synergistic control of cell adhesion by integrins and syndecans. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007; 8(12):957-69. [PMID: 17971838]
- Thodeti CK., Albrechtsen R., Grauslund M., Asmar M., Larsson C., Takada Y., Mercurio AM., Couchman JR. & Wewer UM. ADAM12/syndecan-4 signaling promotes beta 1 integrin-dependent cell spreading through protein kinase Calpha and RhoA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003; 278(11):9576-84. [PMID: 12509413]
- Bass MD., Morgan MR. & Humphries MJ. Integrins and syndecan-4 make distinct, but critical, contributions to adhesion contact formation. Soft Matter 2007; 3(3):372-376. [PMID: 19458789]
- Woods A., Longley RL., Tumova S. & Couchman JR. Syndecan-4 binding to the high affinity heparin-binding domain of fibronectin drives focal adhesion formation in fibroblasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000; 374(1):66-72. [PMID: 10640397]
- Clark RA., An JQ., Greiling D., Khan A. & Schwarzbauer JE. Fibroblast migration on fibronectin requires three distinct functional domains. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2003; 121(4):695-705. [PMID: 14632184]
- Guo F., Debidda M., Yang L., Williams DA. & Zheng Y. Genetic deletion of Rac1 GTPase reveals its critical role in actin stress fiber formation and focal adhesion complex assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2006; 281(27):18652-9. [PMID: 16698790]
- Burridge K. & Wennerberg K. Rho and Rac take center stage. Cell 2004; 116(2):167-79. [PMID: 14744429]
- Guilluy C., Garcia-Mata R. & Burridge K. Rho protein crosstalk: another social network? Trends Cell Biol. 2011; 21(12):718-26. [PMID: 21924908]
- Lamoureux P., Buxbaum RE. & Heidemann SR. Direct evidence that growth cones pull. Nature 1989; 340(6229):159-62. [PMID: 2739738]
- Smith AS., Sengupta K., Goennenwein S., Seifert U. & Sackmann E. Force-induced growth of adhesion domains is controlled by receptor mobility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008; 105(19):6906-11. [PMID: 18463289]
- Balaban NQ., Schwarz US., Riveline D., Goichberg P., Tzur G., Sabanay I., Mahalu D., Safran S., Bershadsky A., Addadi L. & Geiger B. Force and focal adhesion assembly: a close relationship studied using elastic micropatterned substrates. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001; 3(5):466-72. [PMID: 11331874]
- Gomez TM., Robles E., Poo M. & Spitzer NC. Filopodial calcium transients promote substrate-dependent growth cone turning. Science 2001; 291(5510):1983-7. [PMID: 11239161]
- Katsumi A., Milanini J., Kiosses WB., del Pozo MA., Kaunas R., Chien S., Hahn KM. & Schwartz MA. Effects of cell tension on the small GTPase Rac. J. Cell Biol. 2002; 158(1):153-64. [PMID: 12105187]
- Woo S. & Gomez TM. Rac1 and RhoA promote neurite outgrowth through formation and stabilization of growth cone point contacts. J. Neurosci. 2006; 26(5):1418-28. [PMID: 16452665]
- Rottner K., Hall A. & Small JV. Interplay between Rac and Rho in the control of substrate contact dynamics. Curr. Biol. 1999; 9(12):640-8. [PMID: 10375527]
- Bass MD., Roach KA., Morgan MR., Mostafavi-Pour Z., Schoen T., Muramatsu T., Mayer U., Ballestrem C., Spatz JP. & Humphries MJ. Syndecan-4-dependent Rac1 regulation determines directional migration in response to the extracellular matrix. J. Cell Biol. 2007; 177(3):527-38. [PMID: 17485492]
- Sharma A. & Mayer BJ. Phosphorylation of p130Cas initiates Rac activation and membrane ruffling. BMC Cell Biol. 2008; 9:50. [PMID: 18793427]
- Huveneers S. & Danen EH. Adhesion signaling – crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J. Cell. Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 8):1059-69. [PMID: 19339545]
- Kurokawa K., Itoh RE., Yoshizaki H., Nakamura YO. & Matsuda M. Coactivation of Rac1 and Cdc42 at lamellipodia and membrane ruffles induced by epidermal growth factor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004; 15(3):1003-10. [PMID: 14699061]
- Nayal A., Webb DJ., Brown CM., Schaefer EM., Vicente-Manzanares M. & Horwitz AR. Paxillin phosphorylation at Ser273 localizes a GIT1-PIX-PAK complex and regulates adhesion and protrusion dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2006; 173(4):587-9. [PMID: 16717130]
- Kawasaki Y., Senda T., Ishidate T., Koyama R., Morishita T., Iwayama Y., Higuchi O. & Akiyama T. Asef, a link between the tumor suppressor APC and G-protein signaling. Science 2000; 289(5482):1194-7. [PMID: 10947987]
- Katoh H. & Negishi M. RhoG activates Rac1 by direct interaction with the Dock180-binding protein Elmo. Nature 2003; 424(6947):461-4. [PMID: 12879077]
- Berrier AL., Martinez R., Bokoch GM. & LaFlamme SE. The integrin beta tail is required and sufficient to regulate adhesion signaling to Rac1. J. Cell. Sci. 2002; 115(Pt 22):4285-91. [PMID: 12376560]
- Parsons JT., Horwitz AR. & Schwartz MA. Cell adhesion: integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010; 11(9):633-43. [PMID: 20729930]
- del Pozo MA., Alderson NB., Kiosses WB., Chiang HH., Anderson RG. & Schwartz MA. Integrins regulate Rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains. Science 2004; 303(5659):839-42. [PMID: 14764880]
- Del Pozo MA., Kiosses WB., Alderson NB., Meller N., Hahn KM. & Schwartz MA. Integrins regulate GTP-Rac localized effector interactions through dissociation of Rho-GDI. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002; 4(3):232-9. [PMID: 11862216]
- Lu W. & Mayer BJ. Mechanism of activation of Pak1 kinase by membrane localization. Oncogene 1999; 18(3):797-806. [PMID: 9989831]
- Giannone G., Dubin-Thaler BJ., Döbereiner HG., Kieffer N., Bresnick AR. & Sheetz MP. Periodic lamellipodial contractions correlate with rearward actin waves. Cell 2004; 116(3):431-43. [PMID: 15016377]
- Delorme V., Machacek M., DerMardirossian C., Anderson KL., Wittmann T., Hanein D., Waterman-Storer C., Danuser G. & Bokoch GM. Cofilin activity downstream of Pak1 regulates cell protrusion efficiency by organizing lamellipodium and lamella actin networks. Dev. Cell 2007; 13(5):646-62. [PMID: 17981134]
- Oh ES., Woods A. & Couchman JR. Syndecan-4 proteoglycan regulates the distribution and activity of protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1997; 272(13):8133-6. [PMID: 9079625]
- Lim ST., Longley RL., Couchman JR. & Woods A. Direct binding of syndecan-4 cytoplasmic domain to the catalytic domain of protein kinase C alpha (PKC alpha) increases focal adhesion localization of PKC alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 2003; 278(16):13795-802. [PMID: 12571249]
- Koo BK., Jung YS., Shin J., Han I., Mortier E., Zimmermann P., Whiteford JR., Couchman JR., Oh ES. & Lee W. Structural basis of syndecan-4 phosphorylation as a molecular switch to regulate signaling. J. Mol. Biol. 2006; 355(4):651-63. [PMID: 16310216]
- Ng J., Nardine T., Harms M., Tzu J., Goldstein A., Sun Y., Dietzl G., Dickson BJ. & Luo L. Rac GTPases control axon growth, guidance and branching. Nature 2002; 416(6879):442-7. [PMID: 11919635]
- Ren XD., Kiosses WB., Sieg DJ., Otey CA., Schlaepfer DD. & Schwartz MA. Focal adhesion kinase suppresses Rho activity to promote focal adhesion turnover. J. Cell. Sci. 2000; 113 ( Pt 20):3673-8. [PMID: 11017882]
- Schober M., Raghavan S., Nikolova M., Polak L., Pasolli HA., Beggs HE., Reichardt LF. & Fuchs E. Focal adhesion kinase modulates tension signaling to control actin and focal adhesion dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2007; 176(5):667-80. [PMID: 17325207]
- Arthur WT. & Burridge K. RhoA inactivation by p190RhoGAP regulates cell spreading and migration by promoting membrane protrusion and polarity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001; 12(9):2711-20. [PMID: 11553710]
- Tomar A., Lim ST., Lim Y. & Schlaepfer DD. A FAK-p120RasGAP-p190RhoGAP complex regulates polarity in migrating cells. J. Cell. Sci. 2009; 122(Pt 11):1852-62. [PMID: 19435801]
- Bradley WD., Hernández SE., Settleman J. & Koleske AJ. Integrin signaling through Arg activates p190RhoGAP by promoting its binding to p120RasGAP and recruitment to the membrane. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006; 17(11):4827-36. [PMID: 16971514]
- Brouns MR., Matheson SF., Hu KQ., Delalle I., Caviness VS., Silver J., Bronson RT. & Settleman J. The adhesion signaling molecule p190 RhoGAP is required for morphogenetic processes in neural development. Development 2000; 127(22):4891-903. [PMID: 11044403]
- Bass MD., Morgan MR., Roach KA., Settleman J., Goryachev AB. & Humphries MJ. p190RhoGAP is the convergence point of adhesion signals from alpha 5 beta 1 integrin and syndecan-4. J. Cell Biol. 2008; 181(6):1013-26. [PMID: 18541700]
- Vicente-Manzanares M., Newell-Litwa K., Bachir AI., Whitmore LA. & Horwitz AR. Myosin IIA/IIB restrict adhesive and protrusive signaling to generate front-back polarity in migrating cells. J Cell Biol. 2011; 193:381-96. [PMID: 21482721]
- Iwanicki MP., Vomastek T., Tilghman RW., Martin KH., Banerjee J., Wedegaertner PB. & Parsons JT. FAK, PDZ-RhoGEF and ROCKII cooperate to regulate adhesion movement and trailing-edge retraction in fibroblasts. J. Cell. Sci. 2008; 121(Pt 6):895-905. [PMID: 18303050]
- Guilluy C., Swaminathan V., Garcia-Mata R., O’Brien ET., Superfine R. & Burridge K. The Rho GEFs LARG and GEF-H1 regulate the mechanical response to force on integrins. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13(6):722-7. [PMID: 21572419]
- Dovas A., Yoneda A. & Couchman JR. PKCbeta-dependent activation of RhoA by syndecan-4 during focal adhesion formation. J. Cell. Sci. 2006; 119(Pt 13):2837-46. [PMID: 16787950]
- Amano M., Ito M., Kimura K., Fukata Y., Chihara K., Nakano T., Matsuura Y. & Kaibuchi K. Phosphorylation and activation of myosin by Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase). J. Biol. Chem. 1996; 271(34):20246-9. [PMID: 8702756]
- Kimura K., Ito M., Amano M., Chihara K., Fukata Y., Nakafuku M., Yamamori B., Feng J., Nakano T., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A. & Kaibuchi K. Regulation of myosin phosphatase by Rho and Rho-associated kinase (Rho-kinase) Science 1996; 273(5272):245-8. [PMID: 8662509]
- Le Clainche C. & Carlier MF. Regulation of actin assembly associated with protrusion and adhesion in cell migration. Physiol. Rev. 2008; 88(2):489-513. [PMID: 18391171]
- Zaidel-Bar R., Kam Z. & Geiger B. Polarized downregulation of the paxillin-p130CAS-Rac1 pathway induced by shear flow. J. Cell. Sci. 2005; 118(Pt 17):3997-4007. [PMID: 16129884]
- Sanz-Moreno V., Gadea G., Ahn J., Paterson H., Marra P., Pinner S., Sahai E. & Marshall CJ. Rac activation and inactivation control plasticity of tumor cell movement. Cell 2008; 135(3):510-23. [PMID: 18984162]
- Lamarche-Vane N. & Hall A. CdGAP, a novel proline-rich GTPase-activating protein for Cdc42 and Rac. J. Biol. Chem. 1998; 273(44):29172-7. [PMID: 9786927]