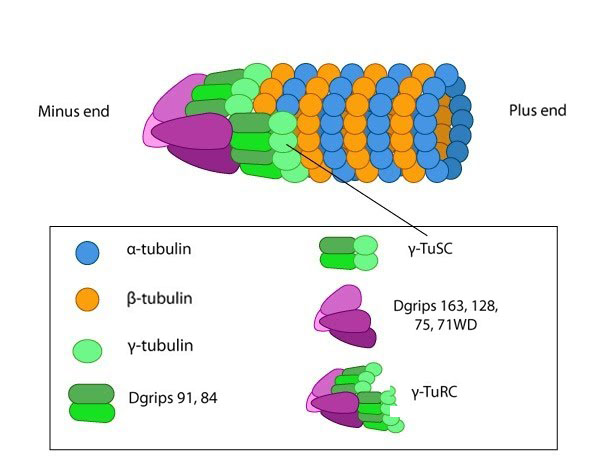
Tubulin and the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC)[Edit]
Microtubules are made up of repeating units of α/β- tubulin heterodimers, which are assembled on a γ-tubulin ring complex (a complex of γ-tubulin and other protein components), during the nucleation phase.
Basic Component: Tubulin
Tubulin is a small globular protein found in all eukaryotic cells. The tubulin family represents about 3-4% of the total protein content in a cell and its members include α-, β-, γ-, δ-, ε-, and ζ-tubulin [1]. Although the different forms of tubulin are similar, they can have different cellular locations and functions. It should be noted that although both actin and tubulin are basic components of the cytoskeleton and possess the ability to hydrolyze NTP, they are evolutionarily distinct with actin being related in structure to hexokinase and tubulins being distantly related to heterotrimeric G-proteins and other GTPases such as Ras [2].Repeating units of ~110kDa α/β-tubulin heterodimers are the primary component of microtubules. Microtubule assembly starts with the assembly of a tubulin complex. Here, γ-tubulin and other protein components form the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC) [2]. The specific cellular roles for additional tubulins such as δ-, ε- and ζ- tubulins are less well known, but they can be found in centrioles and may be involved during mitotic spindle assembly and cell division [3]. Post-translational modification of tubulin such as acetylation, detyrosination, phosphorylation etc. have also been described at length [4]. These modifications may influence the structural properties of microtubules, alter their dynamics and affect how they function within the cell.