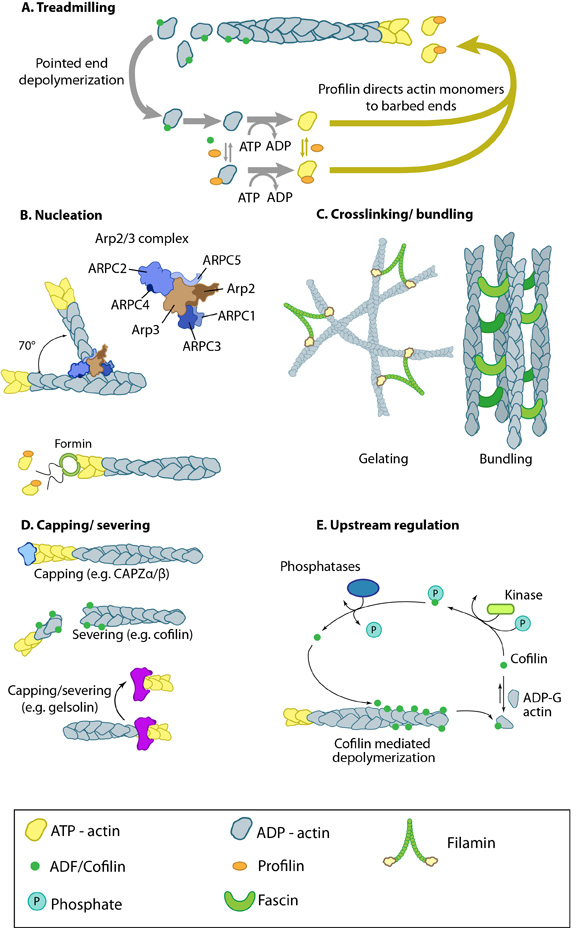
Contents Quiz Test Your Knowledge! Click Here Contribute | Essential Info: Actin Filaments and Mechanotransduction4.4 Actin Filament Structure and FunctionsProteins that bind to actin filaments can influence actin filament assembly and disassembly (see panels A, B, D and E in the Figure below). Actin filaments can also be stabilized (see figure “Tropomyosin stabilizes thin filaments“) and crosslinked by actin binding proteins; the specific type of crosslinking protein will influence not only the type of structure the actin filaments form, but the crosslinking proteins also modulate the physical dynamics of the network (see figure below). In addition, the actin cytoskeleton may be linked through protein complexes to an extracellular substrate; this anchoring allows the actin network to function as a force and tension generator and sensor (see also “focal adhesions” and “contractile bundle“). Proteins with similar functions (e.g. fascin, α-actinin) act cooperatively to enhance the mechanical integrity and responsiveness of the network [1] (reviewed in [2]).Actin filaments generally form the following structures:
Figure: Actin binding proteins influence actin dynamics. (A)Treadmilling of actin filaments can be altered by profilin and ADF which generally increase and decrease the size of actin filaments, respectively. (B) New filaments are nucleated by the ARP2/3 complex, which binds both G-actin monomers and the side of actin filaments to nucleate new filaments or branches. Formins nucleate new filaments by binding G-actin and through cooperation with profilin. (C) Actin cross-linking proteins influence the packing and organization of actin filaments into secondary structures. (D) Capping and severing proteins promote disassembly of actin filaments. (E) Actin filament assembly can be modulated by events such as controlled nucleotide hydrolysis (e.g. ATP on actin) and reversible modifications (e.g. phosphorylation) on components that control actin assembly. Figure adapted from [3]. |
References
- Tseng Y., Kole TP., Lee JS., Fedorov E., Almo SC., Schafer BW. & Wirtz D. How actin crosslinking and bundling proteins cooperate to generate an enhanced cell mechanical response. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005; 334(1):183-92. [PMID: 15992772]
- Carlier MF. & Pantaloni D. Control of actin dynamics in cell motility. J. Mol. Biol. 1997; 269(4):459-67. [PMID: 9217250]
- Baum J., Papenfuss AT., Baum B., Speed TP. & Cowman AF. Regulation of apicomplexan actin-based motility. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006; 4(8):621-8. [PMID: 16845432]