Paxillin[Edit]
Paxillin is a multidomain scaffolding protein that is a key platform for bringing together signaling molecules, structural components, and regulatory proteins that control the adhesion and organization of the internal cytoskeleton for processes such as cell migration (reviewed in [1]). 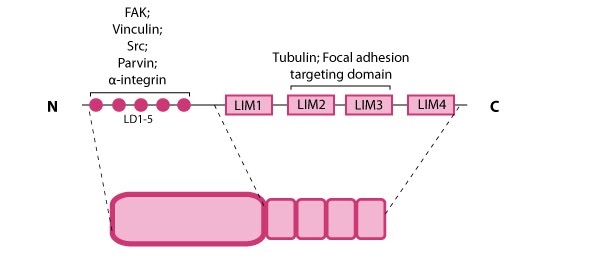 Figure 1. Paxillin: This schematic diagram illustrates the molecular organization of paxillin and provides examples for how paxillin is represented in figures throughout this resource. Relevant domains believed to be important for protein-protein interactions are highlighted (reviewed in [2]). These interactions include FAK, vinculin [3, 4], Src [5], parvin [6],tubulin [7], α-integrin [8, 9, 10], and focal adhesion targeting [11].Paxillin contains five amino-terminal leucine-aspartic acid (LD1-5) motifs and four carboxy-terminal LIM (Lin11, Isl-1, Mec-3) domains; the LD and LIM domains mediate protein-protein interactions with a number of structural and regulatory proteins (see figure at right).
Figure 1. Paxillin: This schematic diagram illustrates the molecular organization of paxillin and provides examples for how paxillin is represented in figures throughout this resource. Relevant domains believed to be important for protein-protein interactions are highlighted (reviewed in [2]). These interactions include FAK, vinculin [3, 4], Src [5], parvin [6],tubulin [7], α-integrin [8, 9, 10], and focal adhesion targeting [11].Paxillin contains five amino-terminal leucine-aspartic acid (LD1-5) motifs and four carboxy-terminal LIM (Lin11, Isl-1, Mec-3) domains; the LD and LIM domains mediate protein-protein interactions with a number of structural and regulatory proteins (see figure at right).
Paxillin contains a number of likely phosphorylation sites for serine/threonine kinases (e.g. protein kinase C) and tyrosine kinases [12] and is phosphorylated in response to various growth factors and adhesion stimuli both in vitro [13, 14] and in vivo [15](reviewed in [1]). Phosphorylation of the LIM domains has been suggested to influence cellular adhesion to fibronectin as well as paxillin localization to focal adhesions [16].
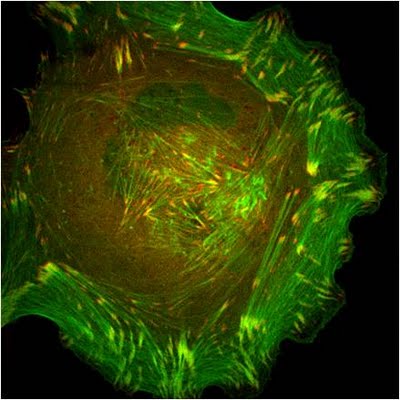 Figure 2. Paxillin Localization: A HFF (human foreskin fibroblast) cell plated on a fibronectin coated glass coverslip, transfected with GFP-LifeAct (green), which labels F-actin in living cells, and mCherry-paxillin (red). It was imaged on Olympus IX81 Inverted microscope using a Perkin Elmer spinning disk at 100x magnification. Image courtesy: Yee Han Tee, Mechanobiology Institute, Singapore.Paxillin binds directly to α-integrins via its amino terminus [17, 18, 19] and it localizes specifically to sites of cell-matrix adhesion (as opposed to cell-cell contacts) (see microphotograph below) [12]. Paxillin also co-localizes with talin and vinculin at the ends of stress fibers [12]. Mechanical tension and force from actin/myosin based contractions along the cytoskeleton network are necessary not only for paxillin recruitment at the adhesion sites during their maturation [20] as well as to stabilize and maintain its localization [21, 22]. These findings, together with evidence suggesting the involvement of paxillin in the detection of shear stress [23], makes paxillin a likely candidate for a mechanosensor.
Figure 2. Paxillin Localization: A HFF (human foreskin fibroblast) cell plated on a fibronectin coated glass coverslip, transfected with GFP-LifeAct (green), which labels F-actin in living cells, and mCherry-paxillin (red). It was imaged on Olympus IX81 Inverted microscope using a Perkin Elmer spinning disk at 100x magnification. Image courtesy: Yee Han Tee, Mechanobiology Institute, Singapore.Paxillin binds directly to α-integrins via its amino terminus [17, 18, 19] and it localizes specifically to sites of cell-matrix adhesion (as opposed to cell-cell contacts) (see microphotograph below) [12]. Paxillin also co-localizes with talin and vinculin at the ends of stress fibers [12]. Mechanical tension and force from actin/myosin based contractions along the cytoskeleton network are necessary not only for paxillin recruitment at the adhesion sites during their maturation [20] as well as to stabilize and maintain its localization [21, 22]. These findings, together with evidence suggesting the involvement of paxillin in the detection of shear stress [23], makes paxillin a likely candidate for a mechanosensor.
In migrating cells, paxillin appears to remodel from older to newer adhesions at the leading edge to become one of the first proteins found at cell-matrix adhesion sites [24]. Paxillin largely contributes to cytoskeleton dynamics by regulating the activity of the Rho family of GTPases and by coordinating their association with specific ligands and downstream effector systems [1]; for example, paxillin-integrin binding is sufficient for regulating signal transduction through Rac1 GTPase [19]. It has also been recently shown to coordinate membrane trafficking and hence directional migration based on physical cues [25].
 Figure 1. Paxillin: This schematic diagram illustrates the molecular organization of paxillin and provides examples for how paxillin is represented in figures throughout this resource. Relevant domains believed to be important for protein-protein interactions are highlighted (reviewed in [2]). These interactions include FAK, vinculin [3, 4], Src [5], parvin [6],tubulin [7], α-integrin [8, 9, 10], and focal adhesion targeting [11].
Figure 1. Paxillin: This schematic diagram illustrates the molecular organization of paxillin and provides examples for how paxillin is represented in figures throughout this resource. Relevant domains believed to be important for protein-protein interactions are highlighted (reviewed in [2]). These interactions include FAK, vinculin [3, 4], Src [5], parvin [6],tubulin [7], α-integrin [8, 9, 10], and focal adhesion targeting [11].Paxillin contains a number of likely phosphorylation sites for serine/threonine kinases (e.g. protein kinase C) and tyrosine kinases [12] and is phosphorylated in response to various growth factors and adhesion stimuli both in vitro [13, 14] and in vivo [15](reviewed in [1]). Phosphorylation of the LIM domains has been suggested to influence cellular adhesion to fibronectin as well as paxillin localization to focal adhesions [16].
Localization and function
 Figure 2. Paxillin Localization: A HFF (human foreskin fibroblast) cell plated on a fibronectin coated glass coverslip, transfected with GFP-LifeAct (green), which labels F-actin in living cells, and mCherry-paxillin (red). It was imaged on Olympus IX81 Inverted microscope using a Perkin Elmer spinning disk at 100x magnification. Image courtesy: Yee Han Tee, Mechanobiology Institute, Singapore.
Figure 2. Paxillin Localization: A HFF (human foreskin fibroblast) cell plated on a fibronectin coated glass coverslip, transfected with GFP-LifeAct (green), which labels F-actin in living cells, and mCherry-paxillin (red). It was imaged on Olympus IX81 Inverted microscope using a Perkin Elmer spinning disk at 100x magnification. Image courtesy: Yee Han Tee, Mechanobiology Institute, Singapore.In migrating cells, paxillin appears to remodel from older to newer adhesions at the leading edge to become one of the first proteins found at cell-matrix adhesion sites [24]. Paxillin largely contributes to cytoskeleton dynamics by regulating the activity of the Rho family of GTPases and by coordinating their association with specific ligands and downstream effector systems [1]; for example, paxillin-integrin binding is sufficient for regulating signal transduction through Rac1 GTPase [19]. It has also been recently shown to coordinate membrane trafficking and hence directional migration based on physical cues [25].