How do formins facilitate filament polymerization?[Edit]
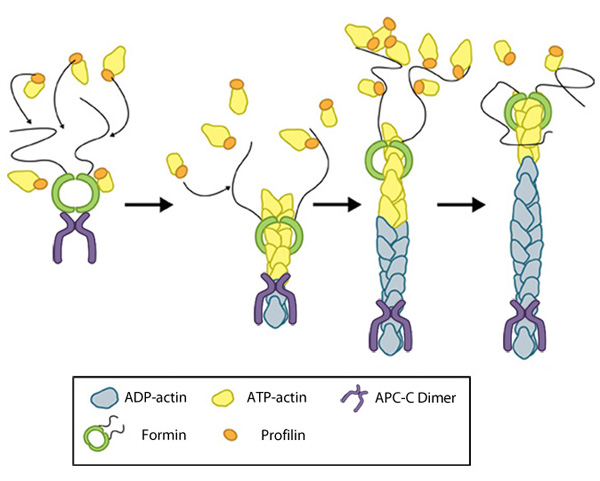 Figure 1. Formin-mediated nucleation of actin filaments: The FH2 domains of the formin dimer (shown in green)
bind to actin monomers to initiate filament assembly. Recent studies
indicate this is assisted, or even mediated, by additional factors such
as APC. The FH1 domains
of the formin dimer (shown as black lines) have short polyproline
sequences that interact with profilin. Profilin binds to both formin and
actin monomers to increase the addition of actin monomers to the barbed
end of the filament.
Figure 1. Formin-mediated nucleation of actin filaments: The FH2 domains of the formin dimer (shown in green)
bind to actin monomers to initiate filament assembly. Recent studies
indicate this is assisted, or even mediated, by additional factors such
as APC. The FH1 domains
of the formin dimer (shown as black lines) have short polyproline
sequences that interact with profilin. Profilin binds to both formin and
actin monomers to increase the addition of actin monomers to the barbed
end of the filament.Next, each formin monomer binds and captures profilin units, which are themselves already bound to G-actin monomers. This interaction is mediated by multiple stretches of polyproline residues within the FH1 domain of formins [4]. This domain is known to range from 15-229 residues, consist of between 35% and 100% proline residues, and contain up to 16 profilin binding sites [5]. Profilin maintains a steady pool of actin monomers by promoting ADP to ATP nucleotide exchange on G-actin[6]. These monomers of ATP-G-actin are then added the growing actin filament. The coupling of formin with the growing end prevents capping and allows continued growth of the filaments [7].