Receptor signaling pathways coordinate steps in motility[Edit]
1) Rac1 activation during early spreading
While α5β1 integrin activates Rac1 by regulating both localization to leading edge and GTP-loading, syndecan-4 influences only the GTP-loading (reviewed in [1]).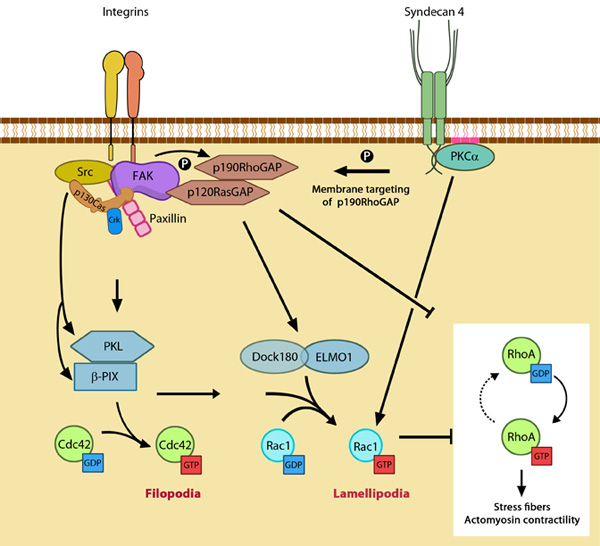 Figure 1. GTPase signaling at the leading edge mediated by integrin
β1 and syndecan-4: Integrin signaling and nascent adhesion formation recruits GEFs such as Dock 180 and PIX for Rac and Cdc42 at the leading edge, activating them. It also inactivates p190RhoGAP while PKC α activation downstream of syndecan-4 sequesters it the membrane to suppress Rho activation. PIP2 is indicated on the membrane in pink. PKCα activation also aids further Rac1 activation and ensures sustenance of Rac1 activity at the leading edge by lipid distributions (not shown). Adapted from [2].
Figure 1. GTPase signaling at the leading edge mediated by integrin
β1 and syndecan-4: Integrin signaling and nascent adhesion formation recruits GEFs such as Dock 180 and PIX for Rac and Cdc42 at the leading edge, activating them. It also inactivates p190RhoGAP while PKC α activation downstream of syndecan-4 sequesters it the membrane to suppress Rho activation. PIP2 is indicated on the membrane in pink. PKCα activation also aids further Rac1 activation and ensures sustenance of Rac1 activity at the leading edge by lipid distributions (not shown). Adapted from [2].During this relocation, the interaction of Rac1 with Rho-GDI is disrupted, allowing p21-activated kinase (PAK) coupling [12, 13]. In the lamellipodium, PAK promotes actin polymerization by inactivating cofilin and aids spreading by suppressing local myosin activity periodically [4, 14, 15]. It also aids actin reorganization in the lamellae [15].
Upon engagement, syndecan-4 forms a ternary complex with PKCα and PIP2 [16, 17] and its oligomerization leads to activation of PKCα [18]. This is a critical step for further GTP-loading of Rac1, restricting Rac1 activity to the leading edge and environment sensing for directional migration [19]. These facilitate downstream signaling for Rac1-mediated actin protrusion [20].
2) Rho suppression at the leading edge
Besides reorganizing actin, Rac-activated PAK also phosphorylates the regulatory light chain (RLC) of myosin II, thus activating bundling of actin and the contractile mechanism. Myosin IIA/IIB-mediated actomysoin bundling generates stable adhesions, inhibit Rac-GEFs in the vicinity by modifying adhesion components that aid their recruitment and thus establish the cell rear [28]. In a force-dependent manner, Rho-specific GEFs have been shown to get activated and recruited to focal adhesions through FAK and Fyn [29, 30] (reviewed in [24]). Thus integrin-signaling pathway activates RhoA. Similarly, a syndecan-4 dependent pathway has been shown for the formation and maintenance of stress fibres, and focal adhesion maturation. Upon syndecan-4 clustering, GTP-loading of RhoA increases in a PKCα-dependent manner [31].
Activation of RhoA further enhances contractility and builds cellular tension through the Rho kinase, ROCK which sustains the myosin RLC phosphorylation [32, 33](reviewed in [34]). Tension-dependent decrease of Rac activity has been demonstrated [35, 36] and is believed to happen through stimulation of a Rac-GAP, ARHGAP22 by the Rho kinase, ROCK [37]. Similarly CdGAP, has been shown to inhibit lamellipodial protrusion and is suggested to do so via its actions on both Rac and Cdc42 [3, 38].